DDR3 vs DDR4 RAM: Is It Worth The Upgrade?
If y'all've been in that location hunting for a new organization to purchase or build by yourself, you must have come beyond the term DDR4 RAM. Every bit far as the market is concerned, the DDR3 is nevertheless, by far, the get-to RAM. We've all been using the DDR3 RAM for near a decade at present, but the market has started witnessing the introduction of DDR4 modules. With new devices coming out each day, is DDR4 actually worth the upgrade, or is it just an expensive newer applied science at comparable performance? How different is the DDR4 from its predecessor exactly? If you've been wondering nigh the aforementioned questions, well don't worry, as nosotros bring to you our detailed comparison of DDR4 vs DDR3 RAM, and whether the newer engineering science really is better or not.
DDR3 vs DDR4: What Has Changed?
-
Physical Changes
To make the jump to newer technologies, the design is probably the first thing that has changed. The DDR3 RAM used a 240-pin package, that has been inverse in the DDR4 RAM. DDR4 has switched to a 288-pin package, which directly goes on to say that at that place volition be an obvious boost in the bandwidth capacity, which we volition discuss farther in the article. Furthermore, since the modules are of the same length, the pin-to-pin distance in the DDR4 RAM has been brought down to 0.85mm, as compared to DDR3's 1.00mm. This further decreases the overall per-pin contact besides.

To accommodate the added pins, the modules have a raised height of 31.25mm, every bit compared to DDR3's 30.35mm. This has been fabricated to brand the routing procedure easier. Additionally, the PCB has been made thicker also, raising the dimensions from 1.0mm on the DDR3 to 1.2mm now, which opens the scope for more signal layers.
-
Operating Voltage
Power consumption is another aspect which manufacturers like to minimize, and cheers to the new DDR4 RAM, it works out quite well for them. The DDR4 RAM operates at a lower voltage of 1.2 volts as compared to DDR3'southward 1.5 volts. While information technology doesn't sound similar a lot, the quoted numbers end upwards saving one-2W per module per system, which for a fully laden home-user desktop might approach 15W at the high finish of savings over DDR3, but for a server farm with 1000 CPUs, this means a 15kW saving. Also, as the demand for battery life in notebooks and ultrabooks increases, using a DDR4 RAM alongside the latest 14nm processors allow for increased usage without rushing towards a power socket.
| DRAM | Depression Voltage | Standard Voltage | Performance Voltage |
| DDR3 | 1.35 V | 1.50 V | 1.65 V |
| DDR4 | 1.05 V | ane.20 V | 1.35 5 |
-
Stability
In DDR3 RAMs, a unmarried voltage source is applied across the whole module. This, in turn, can cause a significant voltage drib, affecting stability. With DDR4 though, things accept inverse. The new pattern that has been implemented in the DDR4 RAMs works by enhancing the lower voltage with the help of voltage reference ICs before each memory chip. This is done in order to ensure that a consistent voltage is practical across each of them individually rather than the whole module at one time. With the assistance of this new design, all the voltage drops are dependent on the IC simply and can be corrected, thus improving the stability of the modules of the DDR4 RAM.
-
Refresh Algorithm
Earlier discussing the differences betwixt the refresh algorithms of DDR3 vs DDR4, let united states discuss a flake about RAMs in brief. Technically, RAMs are of 2 types – Static and Dynamic. The Dynamic RAM, as the name suggests, keeps on refreshing its content every few intervals. Now, depending upon the mode it refreshes, DRAM is divided into multiple types, of which the virtually prominent ane is SDRAM. Synchronous Dynamic Random-Admission Memory (SDRAM) is much faster than previous, conventional forms of RAM and DRAM. Information technology operates in a synchronous mode, synchronizing with the bus within the CPU. At present that we've got that out of the style, let u.s. discuss the differences between DDR3 and DDR4.
In general, SDRAM devices such as DDR3 RAM, utilize auto-refresh (AR) and self-refresh (SR) to perform refreshing of its content. In general, SR is used when idle for power saving, while AR is used when the arrangement is busy. On the other hand,DDR4 supports a low-power auto self-refresh, which does the standard affair of refreshing the contents of retention just uses an adaptive algorithm based on the temperature in society to avoid signal migrate.
In each module, the refreshing modes will adjust each array independently, since the controller must support a fine-grained optimization routine. This is also done to ensure that the parts of the retention that are being used coincide with i some other. This serves as a power besides every bit stability insurance for the years to come.
-
Clock Speed
The clock speed for a RAM represents how fast the RAM tin read or write the data. One of the major differences of DDR3 vs DDR4 RAMs lies in their clocked speeds. Even though for DDR3 RAMs, the clock speed ranges from 800Mhz to 2133Mhz, manufacturers have moved on to brand sure that the lowest clock speed is 1333Mhz for DDR3. That being said, the highest limit remains at 2133Mhz only. DDR4 RAM, on the other manus, picks up where DDR3 left off, with the minimum clock speed set at 2133Mhz and no specific max value. This increase in the clock speeds besides brings almost an overall increase in their bandwidths.
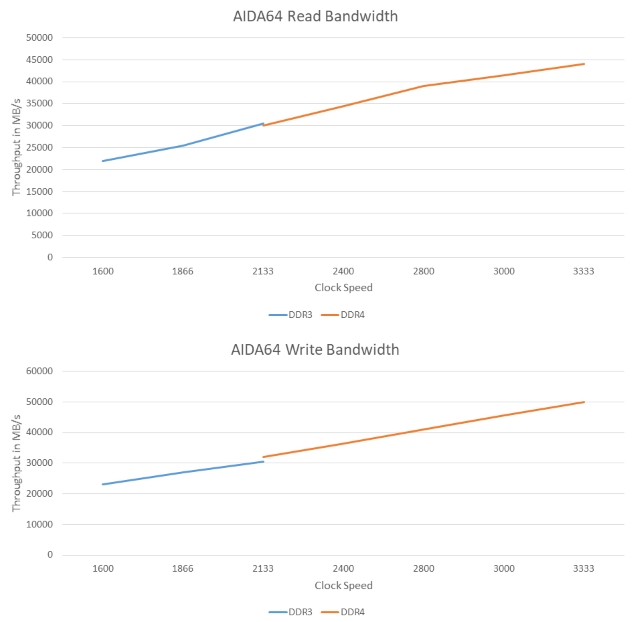
-
Latency
The increased clock speed and bandwidth come forth with an increase in the latency as well. The DDR3-2133 comes with a latency of ~55 nanoseconds. On the other hand, the DDR4-2133 has a latency of ~63 nanoseconds.
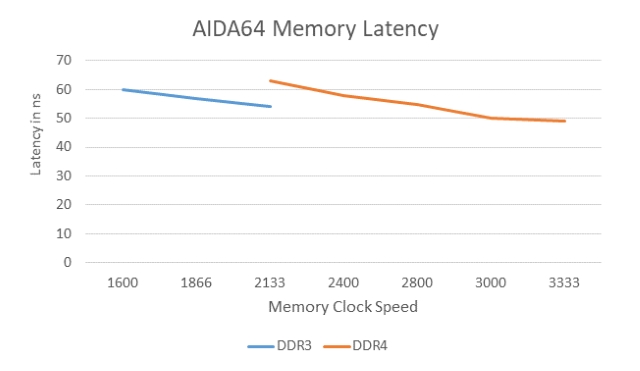
That beingness said, the latency is not that loftier, particularly when the clock speeds and bandwidth abstract the driblet in latency.
-
Memory Chapters
The memory capacity is also another attribute to keep in heed. While for nigh daily usages, 4GB RAM capacity seems to be fine, gamers tend to opt for viii gigs of retentiveness. Additionally, users interested in video editing and similar piece of work tend to go for even college retentiveness capacities. As such, the DDR3 RAM is capped out at 8GB for a unmarried module, while a max capacity of 16GB is available in DIMMs (Dual Inline Memory Modules), which are used in mainframes and workstation systems. On the other hand, DDR4 has no maximum chapters over its retentiveness size, assuasive for the organization to store loftier amounts of data into the memory.
Benchmarks
While benchmarks are never a true testament of real world performances, they do tend to requite some idea about it. We ran a couple of tests to compare the DDR3 RAM vs DDR4 RAM using Handbrake, Adobe Premier, and the PCMark scores.
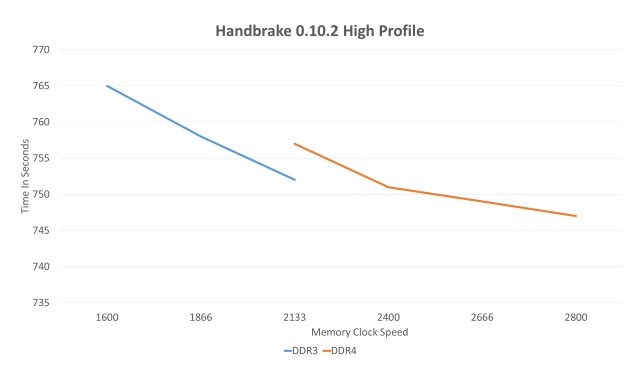
Autonomously from the 2133 Mhz clock speed, the DDR4 seems to be consistently faster across the board, although its advantage does wane fairly early on. The deviation isn't staggering, but information technology's measurable.
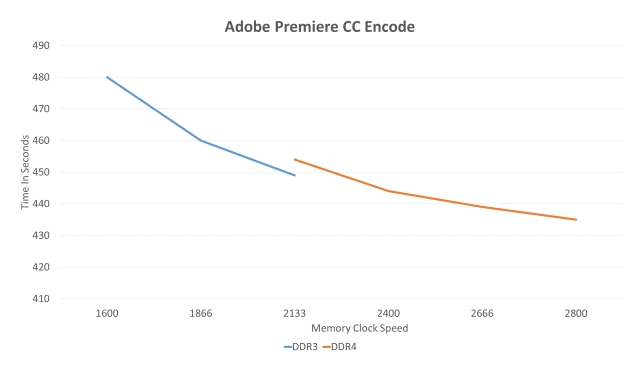
The same trend occurs with Adobe Premiere CC and Adobe Media Encoder, though more pronounced. The DDR4 does outperform the predecessor, but the difference isn't that huge.
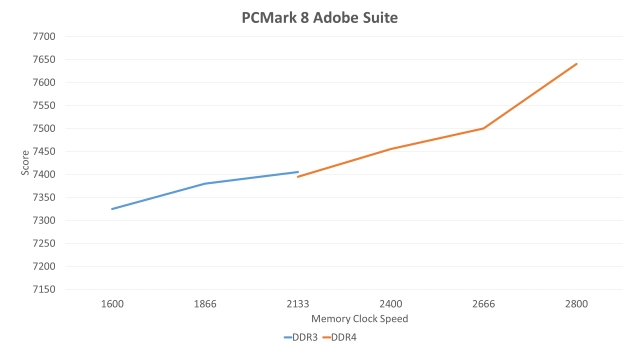
Finally, in the PCMark 8'southward Adobe Suite, the DDR4 is consistently faster and continues to scale up gradually with each speed class. While the difference between DDR3-2133 and DDR4-2133 is very low, merely a single heave up to the next frequency for DDR4 turns the tables around.
Compatibility
Compatibility is a big factor to continue in mind when making your purchase. None of the RAMs are compatible with the other ones, and this has been the example with DDR3 and DDR4 as well. You cannot install a DDR4 RAM onto a DDR3 port or vice versa. Thankfully, motherboard manufacturers make sure to mention what RAM does their system support, thus eradicating whatever confusion. While speaking in general terms, and motherboard congenital between the years 2007 and 2014 is likely to support DDR3 RAM, while models fabricated later on 2014 are more than likely to support the DDR4 module.
Pricing and Availability
The DDR3 standard has been around for almost a decade, whereas the DDR4 modules have merely been here for a couple of years. The DDR4 is the newer and updated technology, and so information technology's a no-brainer that obviously it would be more expensive every bit compared to the DDR3 modules. For instance, you can get the 8GB kit of ADATA DDR3-2133 for $59.29 merely, whereas the comparative DDR4-2133 will set yous back at $91.49, nearly a $30 deviation.
DDR3 vs DDR4: Who Wins?
As mentioned before, DDR4 picks up from where DDR3 left, improving in nearly all the aspects. The DDR4 RAMs have definitely proven to be a worthy successor. While in that location isn't much to divide the ii when both are operating at 2133 Mhz, the higher clock speeds of DDR4 RAM requite it a certain boost over the previous generation of RAMs. The higher raw power, combined with lower ability consumption make the DDR4 a articulate winner against the DDR3 RAM.
Come across Also: NVIDIA G-Sync vs. AMD FreeSync: The Best Variable Refresh Rate Solution?
But Do You Need To Upgrade?
Nosotros've seen that DDR4 does beat the DDR3 RAM in terms of numbers as well equally real-world performance. That existence said, information technology is also notable that the difference between the two isn't that high. If y'all're on a tight upkeep, investing in a DDR3 RAM of college retention module with a faster processor and a ameliorate GPU is more likely to result in improved all-around performances. Or if yous've got the extra greenbacks in paw to spend on the more expensive DDR4 RAM. There is no way that it'd exist a wrong decision, because the fact that it is indeed the future. Either way, the switch to DDR4 is inevitable, one that you'll be making sooner or later.
Well, that's what nosotros remember simply we'd honey to know your thoughts on DDR3 vs DDR4? So, let the states know in the comments section below.
Source: https://beebom.com/ddr3-vs-ddr4-ram/
Posted by: leikerspoicken.blogspot.com


0 Response to "DDR3 vs DDR4 RAM: Is It Worth The Upgrade?"
Post a Comment